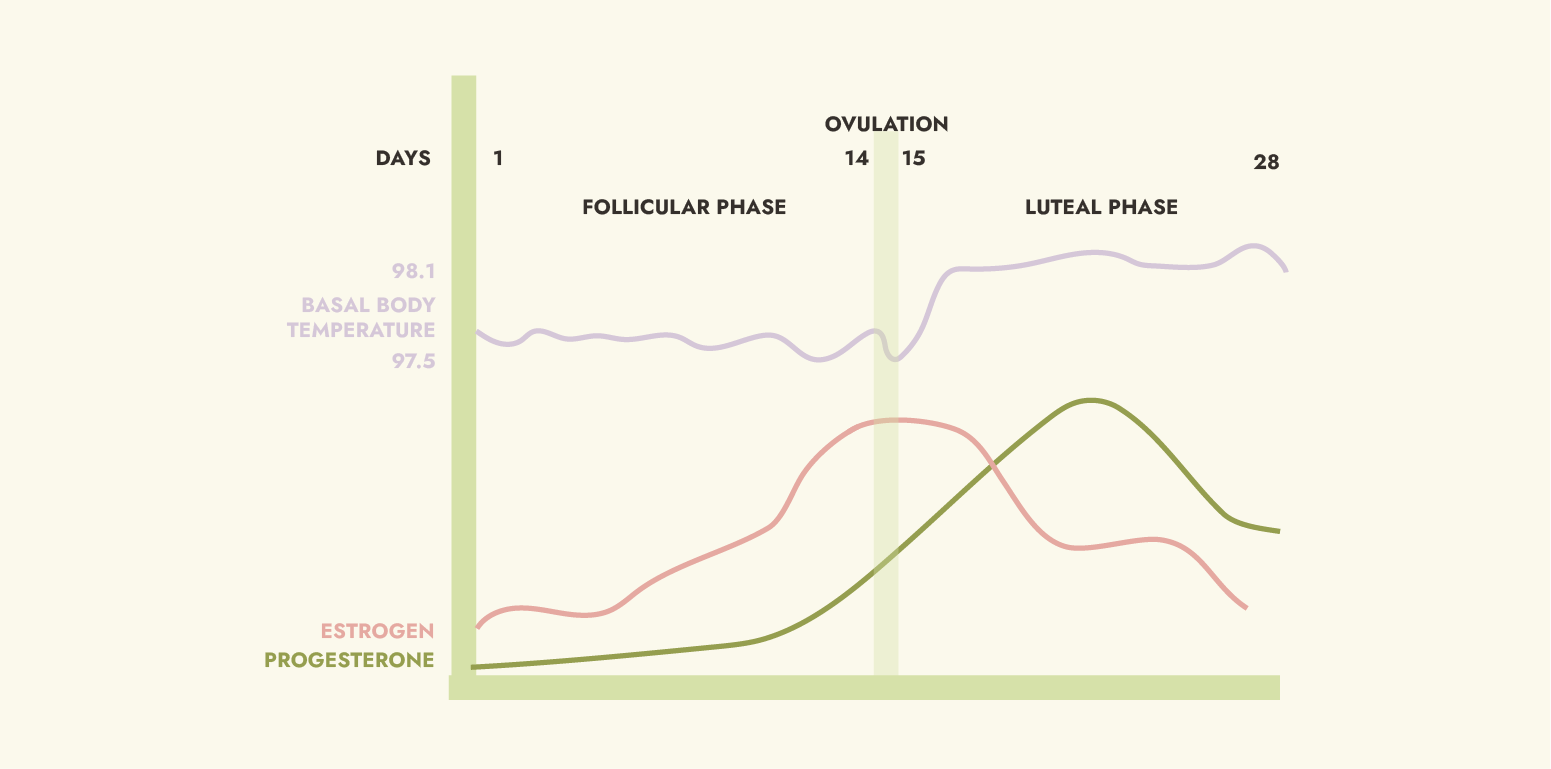
Breaking Down The Cycle
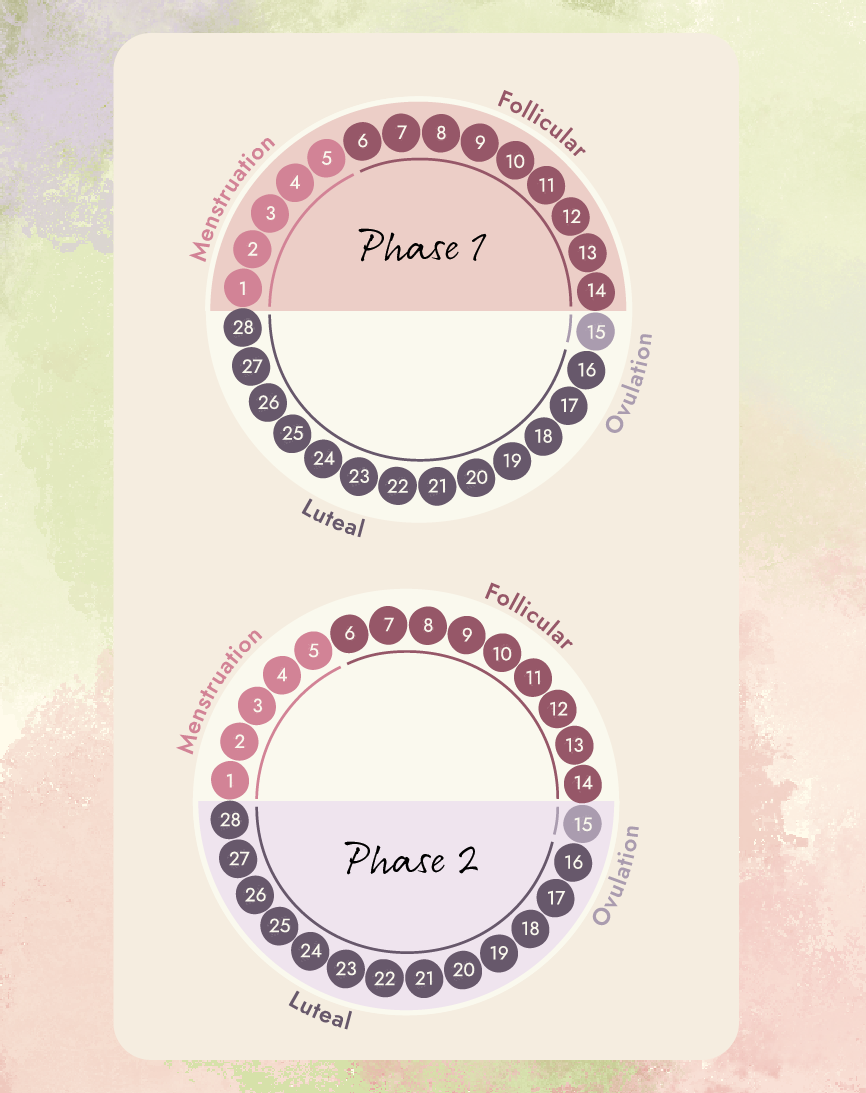
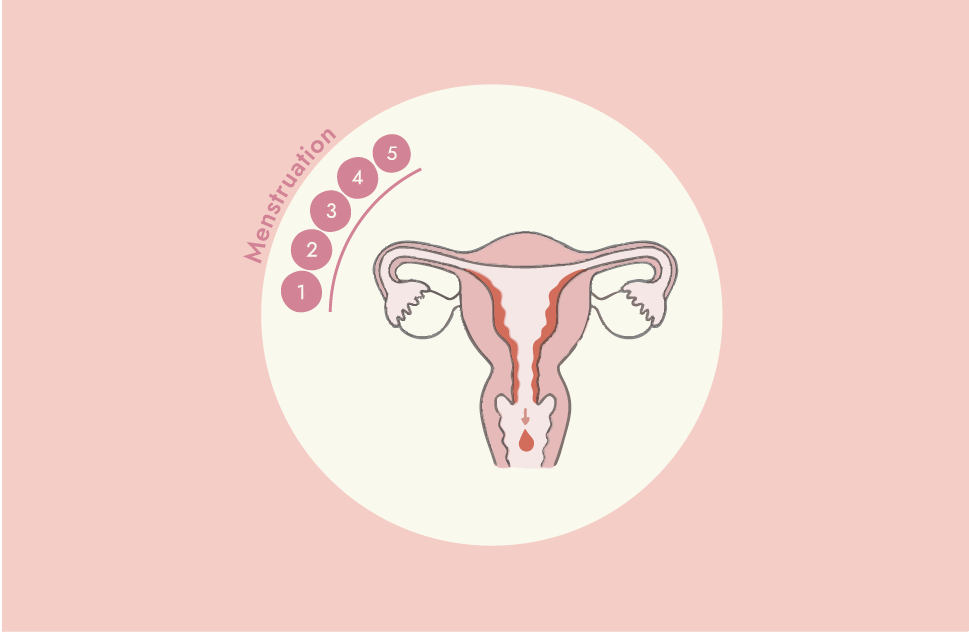
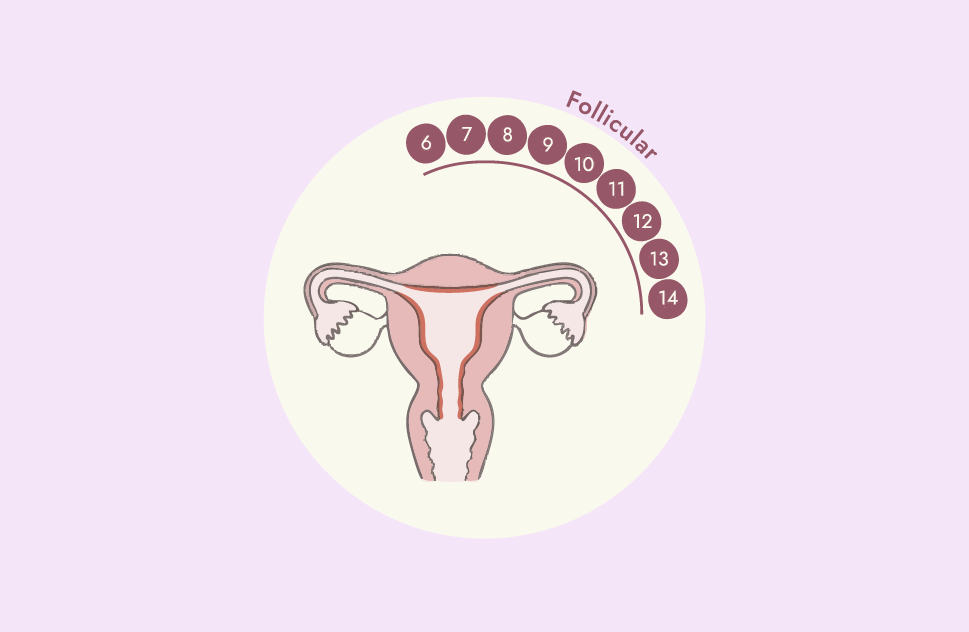
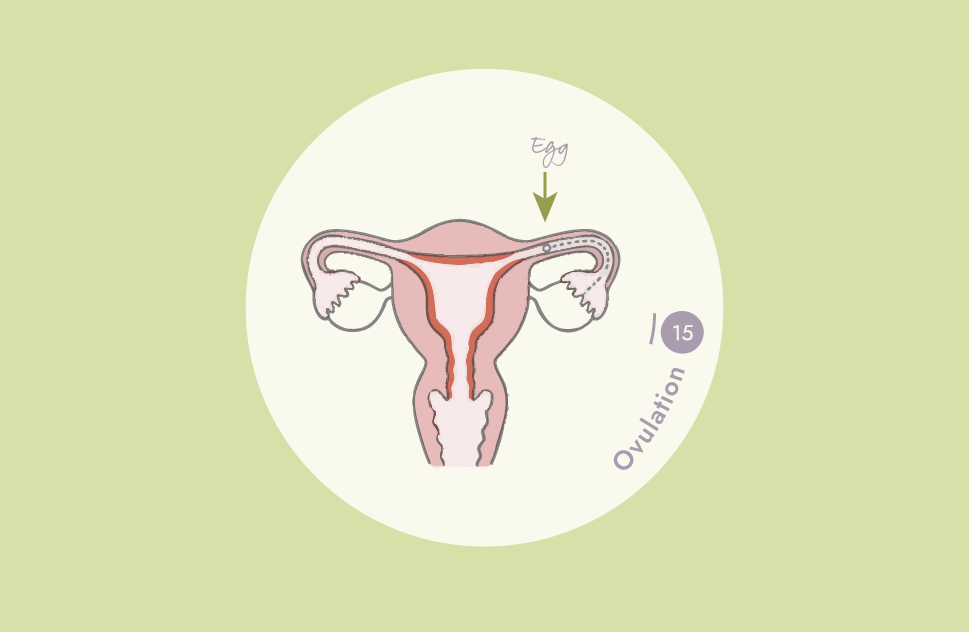
We have designed Cycle Sync to reflect the flow of estrogen and progesterone during the menstrual cycle. You will see below the change from rising estrogen in the first phase, to rising progesterone and breaking down estrogen in the second phase (post ovulation). Mimicking this flow with the right ingredients will help you feel your best and regulate your cycle!